(ideological separation theory) 02023
by
Ozone Bhaguan
for
contributing member
of
Pseudo-isms and the theory of separation of ideology an overview outline
Pseudo-Philosophy vs pseudo-science
Political-Philosophy vs political-science
theoretical-Philosophy vs political-theory
a general inquiry in an attempt to map out the dis-ambugation similarities and distinctions between these terms,that are historically confused and used synonymously.
Inquiry:
seed phrase:
- **fb chat: Can you tell me, do these labels apply?
- Yes or no. If so, to what degree?
- **fb chat There's one question I'd like to ask of your philosophy professor. What is his position on political Theory, does it belong as a branch of philosophy or not? Does political philosophy exist, or is it a pseudo-philosophy as described?
Reply:
- **fb Answer from my professor: What are the arguments that it isn't a branch of philosophy? It is pretty clear to me that we philosophize about political ideas and many philosophers wrote quite a bit about political philosophy.
- rebuttal - write this paper
- interpretation - offered a response, not an answer. inferred a pro-position by requesting the anti-thesis counter argument, and offering a pro-biased bandwagon logical fallacy.
- mis-interpretation: confusing the non-synonymous terms of political theory, political science and political philosophy
Main premise (ideological separation theory)
pro - As, meta-physics; it-IS a philosophy.
claim - meta-physics is-NOT science.
con - As critics claim, meta-physics is: "a pseudo-science".
comparative logic - In the same way, this claim stands to reason, that:
pro - As, political-theory; it-IS a science.
claim - political-theory is-NOT philosophy.
con - As critics claim, political-theory is: "a pseudo-philosophy".
What is political philosophy? wiki-link
What is Pseudo-philosophy? wiki-link
What is political science? wiki-link
What is Psuedo-science? wiki-link
What is political theory? - wiki-link - undefined
- political theory - redirects to normative political theory
- political theory - redirects to Category:Political_theories
What is philosophical theory - wiki-link - undefined
main contention - (ideological separation theory)
confusion of actions -
philosophy as a noun - talking about the quality or quantity of a topic as an object, subject. (pseudo)
philosophy as a verb - performing any standard action or method of examination of the topic (actual).
see also - theory vs practice
reference - web-link - what are characteristics of pseudo-science?
Excerpt -
- The term pseudoscience is often considered pejorative, particularly by purveyors of it, because it suggests something is being presented as science inaccurately or even deceptively. Therefore, those practicing or advocating pseudoscience frequently dispute the characterization.
11 CHARACTERISTICS OF PSEUDOSCIENCE
- Is unfalsifiable: It can’t be proven wrong.
- Relies heavily on anecdotes: The evidence largely comes from personal experiences and testimonials.
- Cherry picks evidence: Uses favorable evidence while ignoring or minimizing disconfirming evidence.
- Uses technobabble: Words that sound scientific but are used incorrectly or don’t make sense.
- Lacks a plausible mechanism: There’s no way to explain how the claim might work based on existing knowledge.
- Resists change: Doesn’t self-correct or progress.
- Makes extraordinary/exaggerated claims: Promises extraordinary benefits with insufficient evidence.
- Professes certainty: Talks of “proof” and presents ideas with complete confidence.
- Commits logical fallacies: Arguments contain errors in reasoning.
- Lacks adequate peer review: Avoids critical scrutiny by the scientific community.
- Claims there’s a conspiracy to suppress their ideas: Criticism by the scientific community is a conspiracy
quora link: what is psudeo-philosophy?
Sage: AI bot: response:
- Pseudo-philosophy refers to ideas or concepts that present themselves as philosophy, but do not adhere to the rigorous standards of critical thinking, evidence, and logical reasoning that are central to the field of philosophy. These ideas may be based on personal belief, intuition, or faith, rather than on objective evidence and logical reasoning. They may also be characterized by superficial or superficial understanding of the subject matter, or by a lack of coherence or consistency. Examples of pseudo-philosophy include conspiracy theories, New Age spiritualism, and self-help gurus. It is important to be critical and skeptical of any claims that are presented as philosophy, and to approach them with a healthy dose of skepticism and a willingness to question assumptions.
Excerpt:
- How does the bandwagon fallacy work? The bandwagon fallacy works by arguing that because so many other people hold a specific belief, that belief can't be wrong. It makes the listener or reader second-guess any doubts they have about that belief and potentially wonder if they're the one with the misinformed opinion.
reference link: bandwagon fallacy
main premise - (ideological separation theory)
possible solution: using the scientific method to examine the topic over talking about the subject
- **Fb chat: To qualify a theory as science: she has to offer a reasonable explanation as to the observed conditions, offer a theory to describe predictions and offer experimental methods to measurable outcomes. For example: as a theory western imperialism is inherently destructive and is detrimental for humanity. Oligarchy is inhumane. Radical feminist theory suggests that the global adoption of radical feminism can repair the social damage, and reduce the impact western imperialism has on humanity. Matri-archy, or in this case neighbor-ocracy is more humane. Essentially any theory that can follow the scientific method
Excerpt: 5+1 scientific methods
At the core of biology and other sciences lies a problem-solving approach called the scientific method. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step:
- Make an observation
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions
political philosophy - main
What is political philosophy? wiki-link
Excerpt -
- Political philosophy is a branch of philosophy,[2] but it has also played a major part of political science, within which a strong focus has historically been placed on both the history of political thought and contemporary political theory (from normative political theory to various critical approaches).
political philosophy - Wiki-link - main - History - Ancient India
Excerpt -
Indian political philosophy in ancient times demarcated a clear distinction between (1) nation and state (2) religion and state. The constitutions of Hindu states evolved over time and were based on political and legal treatises and prevalent social institutions. The institutions of state were broadly divided into governance, diplomacy, administration, defense, law and order. Mantranga, the principal governing body of these states, consisted of the King, Prime Minister, Commander in chief of army, Chief Priest of the King. The Prime Minister headed the committee of ministers along with head of executive (Maha Amatya)
Supporting Premise: pro-thesis - separation of ideology
- - one of the early historical examples noted of the attempt to separate social activities from state authority in ancient India.
- monarchy/tate
- administration/state
- military/state
- church/state
political philosophy - Wiki-link - main - History - Islam
excerpt:
- Early Islamic philosophy emphasized an inexorable link between science and religion, and the process of ijtihad to find truth—in effect all philosophy was "political" as it had real implications for governance.
Supporting Premise- (ideological separation theory)
anti-thesis - centralized ideology as theology - state as a religion - reinforces the unity of church and state - is detrimental for diversity of ideology - antagonistic - (ideological separation theory)
- This wiki entry serves as an early example of how active attempts were made to use theology to yoke - to bind - hold together - to unify all thought under a centralized religious ideology and authority.
political philosophy - Wiki-link - main - History - Ancient China
excerpt:
- Taoism advocated a proto-anarchism. Legalism was the dominant political philosophy of the Qin Dynasty, but was replaced by State Confucianism in the Han Dynasty. Each had religious or mythic aspects as well that played into how they viewed fairness in governance.
- supporting premise; synth-thesis - taoism, as an early form of proto-anarchism is closer to my personal position as a political theory
**fb chat This is closer to my (*personal) position. Taoism advocated a proto-anarchism
excerpt: wiki-link - Philosophical anarchism
- Philosophical anarchism is an anarchist school of thought which focuses on intellectual criticism of authority, especially political power, and the legitimacy of governments.[1][2][3] The American anarchist and socialist Benjamin Tucker coined the term philosophical anarchism to distinguish peaceful evolutionary anarchism from revolutionary variants.[4] Although philosophical anarchism does not necessarily imply any action or desire for the elimination of authority, philosophical anarchists do not believe that they have an obligation or duty to obey any authority or conversely that the state or any individual has a right to command. Philosophical anarchism is a component especially of individualist anarchism.[5]
political theory - main
What is political theory? undefined
- political theory - redirects to normative political theory
- political theory - redirects to Category:Political_theories
excerpt - web-link
Political theory involves the study of the history of political thought as well as problems in contemporary political life that have a philosophical dimension. The Princeton political theory faculty, one of the largest in the U.S., has depth in both aspects of the subject.
Main premise - (ideological separation theory)
- **fb The premise, I'm suggesting (*there) is an outside, malignant force imposing (political theory), IE, state authority into political philosophy. This suggests that Islamic state theology outright enforces it.
- (*quote) " Early Islamic philosophy emphasized an inexorable link between science and religion, and the process of ijtihad to find truth—in effect all philosophy was "political" as it had real implications for governance." (*end quote)
- **fb In other words, theology, hence, IE = imperialism/state-ism has an agenda to discredit science and deny the separation of philosophy and science. To maintain the yoke of church and state, interject theology into science, interject theology into secular debate, Interject political theory into philosophy.
- **fb Philosophy is about first conditions. Politics is about the results of those conditions, measuring the science of, the effective enforcement of those values.
Main objections - (ideological separation theory)
- the pursuit of Divine truth as theology or the pursuit of human truth as we, mere mortals, as agents of free will, as free thinking conscious agents can best describe, as feeble as it is.
Contentions -( ideological separation theory)
- As a proponent of radical philosophy, I would prefer: to explore how we can separate these conditions into categorically distinct parameters.
- philosophy and the state
- theology and the state
- science and the state
- Health and the state
- Social contract law and the state
- Economy and the state
- Self-regulation and the state
- Administration and the state
- Justice and the state
- Technology and the state
- Diplomacy and the state
- Mobility and the state
- Education and the state
What is history political science? wiki-link
Excerpt:
- While the term "political science" as a separate field is a rather late arrival in terms of social sciences, analyzing political power and the effects that it had on history has been occurring for centuries. However, the term "political science" was not always distinguished from political philosophy, and the modern discipline has a clear set of antecedents
who are the founding fathers of political science? wiki-links
excerpt: who: founding fathers of political science
- Founders of political science are often said to include Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and Niccolo Machiavelli, among others.
who:
- Niccolo Machiavelli - wiki-link- state influences - central authority
- John locke - wiki-link - esoteric influences - enlightenment era
- thomas hobbes - wiki-link - undefined
What are the differences between political philosophy and political theory?
Reference link:
Excerpt:
-
The Source of the Difference between Political Philosophy and Political Theory
-
The main reason for the distinction between political theory and political philosophy is the emergence of positivism in the nineteenth century. The application of positivism in political science led to an attempt to differentiate between political philosophy and political theory.
On the Distinction between Political Philosophy and Political Theory
excerpt:
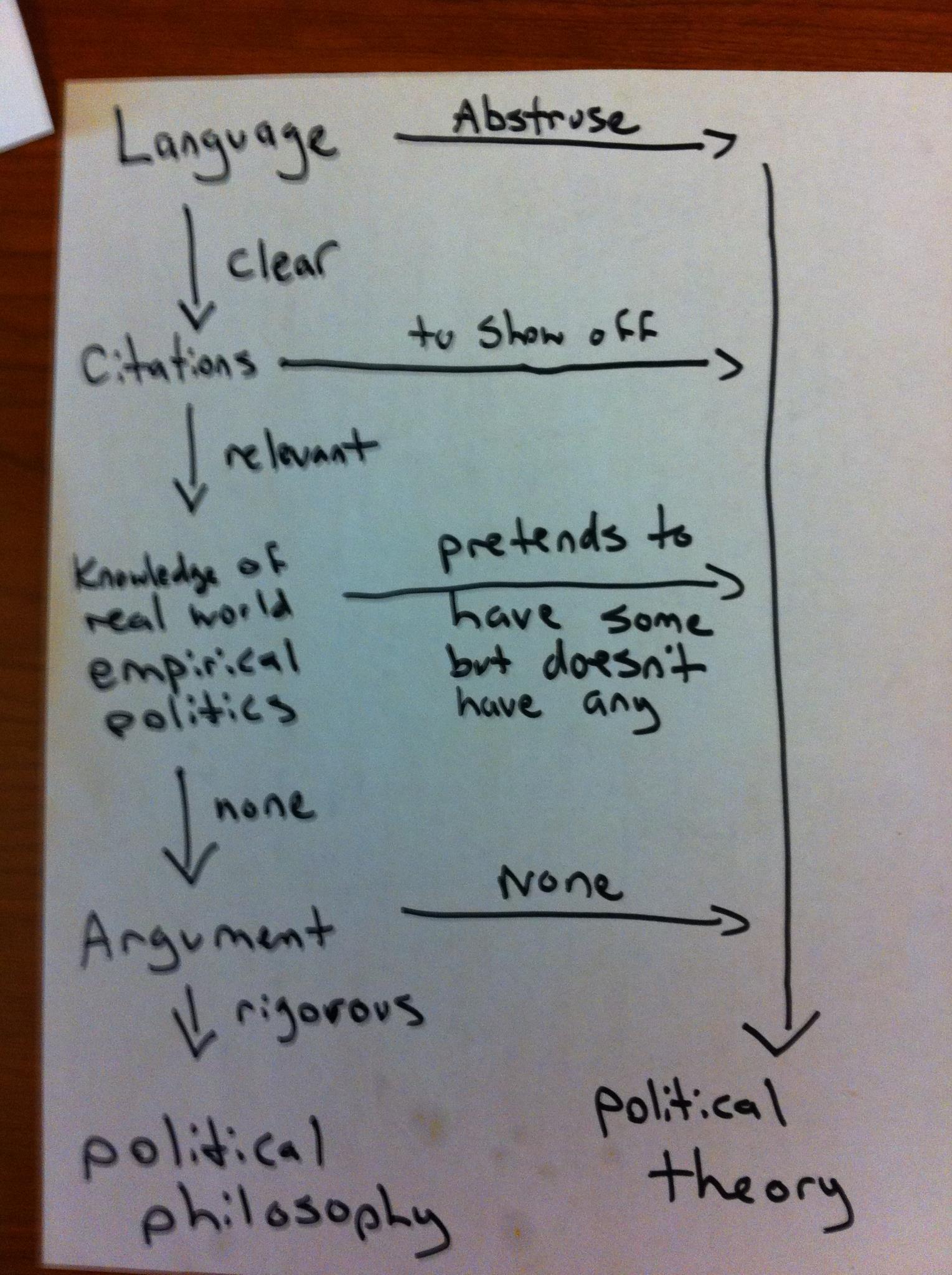
- On the view Brennan develops, political philosophy isn’t sensitive to empirical facts and it doesn’t pretend to be. Whereas, political theory claims that it engages in analysis of empirical facts but doesn’t actually do so (at least not in any serious way). Political philosophy is clear and well argued. Political theory is neither of these things. In short, on Brennan’s view, “political philosophy” is synonymous with “good” and “political theory” is synonymous with “bad.”
Political Philosophy vs. Political Theory Explained in a Flowchart
INSERT FLOW CHART HERE
see flow chart below
main premise - (ideology separation theory)
**reiterate the inquiry:
- **fb chat -The question was to determine what side of the fence he's on.
- What is his position?
- What is his professional perspective?
- reiterate - does it belong there?
- Does the science of, (political theory) belong - in the same category as political philosophy?
- or not?
- Does the (activity of) - (discussion of) valid & rigorous political philosophy, happen?
- rebuttal - My personal opinion = Yes.
main premise - (ideology separation theory)
- rebuttal - I can agree to say - *(valid & rigorous political philosophy activity) exists.
- clarification- as opposed to - ,*(invalid & non-rigorous political theory) devolves into a spectrum of misinformation that occurs with rather alarming frequency and virulent persistence.
- this is a hallmark symptom of - (information disorder theory)
- what is information disorder theory? - wiki-link
Conjecture - (ideological separation theory)
Post-Modern interpretation suggests -
- how before why - science is prioritized before philosophy in this relevant hierarchy
History suggests -
- why before how - philosophy is prior to science as an evolutionary progression of human thought.
ancient history suggests -
- who before why - theology is the foundation from which original ideology built on. the invention of the “mysterious other” to explain unknown phenomena
Post-Modern view:
It appears that radical philosophy is a subset of political science, women's studies, critical theory, social philosophy
Critics who claim pusdeo-philosopher
example wiki-link
- Critics of ayn rand - Excerpt:3.6. - Objectivism
- Journalist Jonathan Chait used the term to criticize the work of Ayn Rand in "Ayn Rand's Pseudo-Philosophy", an article in The New Republic, in which he wrote, "She was a true amateur who insisted on seeing herself as the greatest human being who ever lived because she was almost completely unfamiliar with the entire philosophical canon."[22] Physicist and philosopher of science Mario Bunge classified Rand as a "mercenary", among those who "seek to defend or propagate a doctrine rather than an analyzing ideas or searching for new truths",[23]
what is radical positivism? web-links
excerpt
- Radical positivism (sometimes referred to as inductivist positivism) basically adopts a view that facts are the basis of science. The only admissible evidence for science is that which can be regarded as observable fact. Verification is then dependent on the ultimate authority of such facts. Generalizations are then derived inductively from the particular observations and experiences.
what is inductivism? wiki-links
excerpt
- inductivism is the traditional and still commonplace philosophy of scientific method to develop scientific theories.[1][2][3][4] Inductivism aims to neutrally observe a domain, infer laws from examined cases—hence, inductive reasoning—and thus objectively discover the sole naturally true theory of the observed.[5]
For further study: Additional references:
What is radical philosophy?
https://www.radicalphilosophy.com/
Radical Philosophy is a tri-annual peer-reviewed academic journal of critical theory and philosophy. It was established in 1972 with the purpose of providing a forum for theoretical work which was emerging in the wake of the radical movements of the 1960s, in philosophy and other fields. The journal is edited by an "editorial collective".
Radical philosophy:
Political science:
Critical theory:
Social philosophy:
Associations: http://www.radicalphilosophyassociation.org/
Beyond anthrocentrism:
Applied philosophy
What is practical philosophy?
what is social science? wiki-link
what is Category:Sociological theories? wiki-links
- The main article for this category is Sociological theory.
- This category contains various sociological and sometimes interdisciplinary theories and paradigms. For the different variants of theories or paradigms, please see its individual sub-category. For philosophical theories about society see Category:Social theories.
sub-categories -
what is social development theory? wiki-links
what is feminist theory? wiki-links
what is positivism? wiki-links
IE- flow chart